 Discover how PCB drilling plays a crucial role in modern electronics by facilitating smooth circuit connections and ensuring reliable device performance. Gain practical knowledge and expert advice to enhance your manufacturing process.
Discover how PCB drilling plays a crucial role in modern electronics by facilitating smooth circuit connections and ensuring reliable device performance. Gain practical knowledge and expert advice to enhance your manufacturing process.
Introduction
PCB drilling is a vital process in modern electronics, enabling electrical connections within circuit boards by creating precise holes for vias and component leads. This ensures reliable functionality across devices. Precision and efficiency are crucial, requiring advanced tools and attention to detail. This article explores various PCB drilling techniques, from mechanical to laser methods, and addresses challenges in maintaining accuracy. It offers practical insights to optimize drilling processes, making it valuable for both experienced professionals and newcomers looking to improve manufacturing efficiency.
The Essentials of PCB Drilling
PCB drilling is essential in electronics manufacturing, creating electrical pathways in printed circuit boards (PCBs). Precise techniques and tools are vital for achieving intricate designs, ensuring product reliability and optimal performance in competitive markets.
What Is PCB Drilling, and Why Does It Matter?
PCB drilling creates precise holes (vias) in circuit boards to allow electrical connections and component placement. Drilled before lamination and electroplating, vias ensure seamless electrical signal flow between layers. PCB drilling also forms mouse bites for efficient processing of large batches.
Key applications of PCB drilling include:
Consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications.
Multilayer boards and compact circuit designs.
Advanced devices like smartphones, medical equipment, and IoT solutions.
Long-term durability and high performance in demanding environments.
PCB designers export drill files to manufacturers using automated drilling techniques (CNC machines or lasers) for precise results.
Types of PCB Drilling: Techniques and Tools
Mechanical Drilling
Uses high-speed rotary drill bits for cost-effective, high-volume production. It can drill holes as small as 6 mils but is less accurate than other methods. The lifespan varies based on material hardness.
Laser Drilling
A non-contact method using lasers for precise hole formation, ideal for small holes (as small as 2 mils). It offers high accuracy but is more expensive and challenging with different PCB layer properties.
Manual Drilling
A simple, hands-on technique often used for DIY projects. It is cost-effective but lacks precision and safety compared to mechanical and laser drilling methods.
Optimizing PCB Drilling Processes
To achieve precision and efficiency in PCB drilling, essential tools and materials include:
CNC Machines: Provide automated control for precise drilling and enable real-time adjustments to enhance performance and accuracy.
Drill Bits: High-speed steel (HSS) and carbide bits are durable and efficient, with specialized coatings extending their lifespan.
Lasers: CO2 and UV lasers offer exceptional precision, ideal for micro-scale applications and complex multilayer boards.
Material Compatibility: Ensuring drill bits and lasers are compatible with materials like FR4 or aluminum is crucial for optimal results and tool longevity.
By selecting the right equipment and ensuring material compatibility, manufacturers can reduce errors and improve drilling performance.
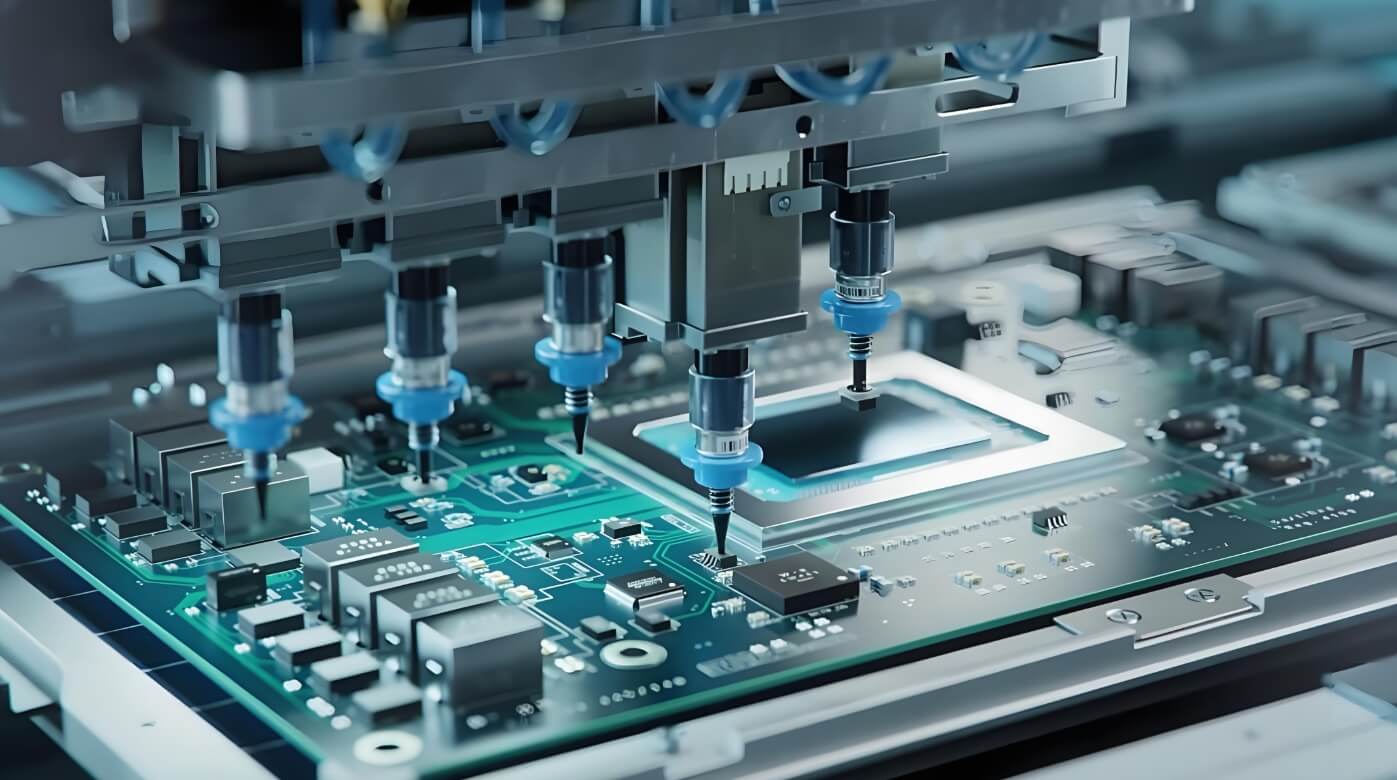
PCB Drilling
Precision Drilling Techniques: Best Practices
For optimal PCB drilling results, follow these best practices:
Choose the Right Drill Bits: Use compatible high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide bits for mechanical drilling.
Calibrate Machine Settings: Adjust spindle speed and feed rate based on material properties and hole diameter.
Secure the PCB Material: Ensure stable clamping to prevent movement during drilling.
Optimize Drilling Depth: Set precise depth controls to protect the board and underlying layers.
Inspect and Replace Worn Tools: Regularly check and replace worn bits to maintain accuracy.
Maintain Equipment: Clean and service drilling machines for consistent performance.
By following these guidelines, manufacturers can achieve high-quality, precise drilling results.
Types of Holes Created During PCB Drilling
PCB drilling creates various types of holes, each serving a distinct purpose:
Connection Holes: These holes provide electrical connectivity between different components and layers.
Through-holes: Penetrate the entire board, enabling connections between layers.
Blind Vias: Connect external layers to internal layers.
Buried Vias: Connect internal layers within the board.
Microvias: Small, laser-drilled holes for high-density connections.
Mechanical Holes: These holes are used for mounting and securing PCBs and do not require electrical connections.
Support component mounting (e.g., brackets).
Aid thermal conductivity by dissipating heat from high-power components.
Provide tooling holes for equipment alignment during manufacturing.
Reinforce the structural integrity of the PCB.
Key Considerations During PCB Drilling
Positional Deviation: Inaccurate hole placement can cause fractures. Proper maintenance and laser drilling can help prevent this.
Layer Separation: Improper drilling weakens the PCB structure. Work with experienced manufacturers.
Burr Formation: Burrs are caused by worn drill bits, heat, and material variations. Use sharp bits, correct speeds, and coolants to prevent burrs.
Drill-bit Breakage: Excess pressure can break drill bits, leading to higher costs. Use strong, durable bits to avoid frequent replacements.
Minimizing Errors and Ensuring Durability
To achieve error-free and durable PCB drilling results, implement the following quality control measures:
Establish Quality Control Checks: Monitor the drilling process in real-time to identify and address deviations immediately.
Test Drill Accuracy: Use precision tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) to verify hole positions and dimensions.
Inspect Drilled Holes: Check for burrs, cracks, or uneven edges that could impact performance.
Verify Depth Accuracy: Use depth gauges to ensure drilling depths meet design specifications.
Document Results: Record quality checks and testing outcomes to address recurring issues.
Train Personnel: Ensure operators are trained on advanced equipment and best practices.
By following these steps, manufacturers can enhance accuracy and durability in PCB drilling.
PCB drilling is a crucial process in electronics manufacturing, requiring precision, the right techniques, and appropriate tools. As drilling technology and materials advance, manufacturers will be able to handle more complex designs and tighter tolerances with greater ease. By adopting best practices and proactively addressing challenges, manufacturers can improve production outcomes and maintain high-quality standards. This guide provides essential insights, helping professionals refine their techniques for sustained excellence in PCB drilling.