Electronic Manufacturing Services(EMS), also known as Electronic Contract Manufacturing (ECM), refers to a electronics manufacturer that provides manufacturing, procurement, partial design, and logistics services to electronic product brand owners.
Compared to OEM or ODM manufacturers who only provide product design and OEM production, Electronic Manufacturing provides knowledge and management services, such as material management, logistics transportation, and even product maintenance services.
Electronic manufacturing is one of the industries with the deepest division of labor in the world, involving multiple levels and fields, with a wide variety of product types. The upstream of electronic manufacturing is the electronic component manufacturing industry, which mainly includes chips, PCBs, passive components, connectors, etc. The upstream electronic component manufacturing industry is the fundamental supporting industry for electronic manufacturing, and its technological level, production scale, and manufacturing costs directly affect the development of electronic manufacturing. The downstream of Electronic Manufacturing includes electronic product brands in various fields such as automotive electronics, consumer electronics, industrial control electronics, and medical electronics. Changes in market demand in the downstream field directly affect the development of Electronic Manufacturing services.
Electronic manufacturing process
Raw material procurement and evaluation: The primary step in electronic manufacturing is to purchase various raw materials, such as semiconductor materials, metals, plastics, etc. The selection and evaluation of suppliers play a crucial role in ensuring material quality and reliability to ensure the stability of the production process.
Design and development: Product design and development are crucial steps before manufacturing. Engineers and design teams use CAD (Computer Aided Design) software to create 3D models of products and conduct functional and reliability testing. This ensures that the product meets the expected performance standards during the manufacturing process.
Manufacturing process planning: Manufacturing process planning involves determining production line layout, equipment selection, and process arrangement. This helps to maximize production efficiency, reduce production costs, and ensure quality consistency.
Manufacturing: The manufacturing stage includes various processes such as cutting, stamping, welding, spraying, etc. In semiconductor manufacturing, key processes include wafer preparation, photolithography, and thin film deposition. Each step requires precise instruments and strict control to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
Assembly: In electronic manufacturing, assembly is the process of assembling various components into the final product. This involves mechanical assembly, welding, installation of electronic components, etc. The precise assembly process is crucial for ensuring the reliability and stability of the product.
Testing and Quality Control: Electronic Manufacturing is completed, the product needs to undergo strict testing and quality control processes. Various testing methods, such as functional testing, reliability testing, environmental testing, etc., are used to verify whether the product meets performance and reliability requirements.
Packaging and Distribution: After completing testing and quality control, the product needs to be properly packaged to ensure that it is not damaged during transportation and storage. Then, the product is distributed to sales channels and prepared for the market.
After sales support: Electronic manufacturing is not just about production, and after-sales support is also an indispensable part. Manufacturers need to provide repair, maintenance, and technical support to meet customer needs and establish long-term partnerships.
Environmental Protection and Sustainability: In electronic manufacturing, environmental protection and sustainability issues are increasingly receiving attention. Manufacturers need to pay attention to waste management, energy consumption, and material recyclability to reduce their impact on the environment.
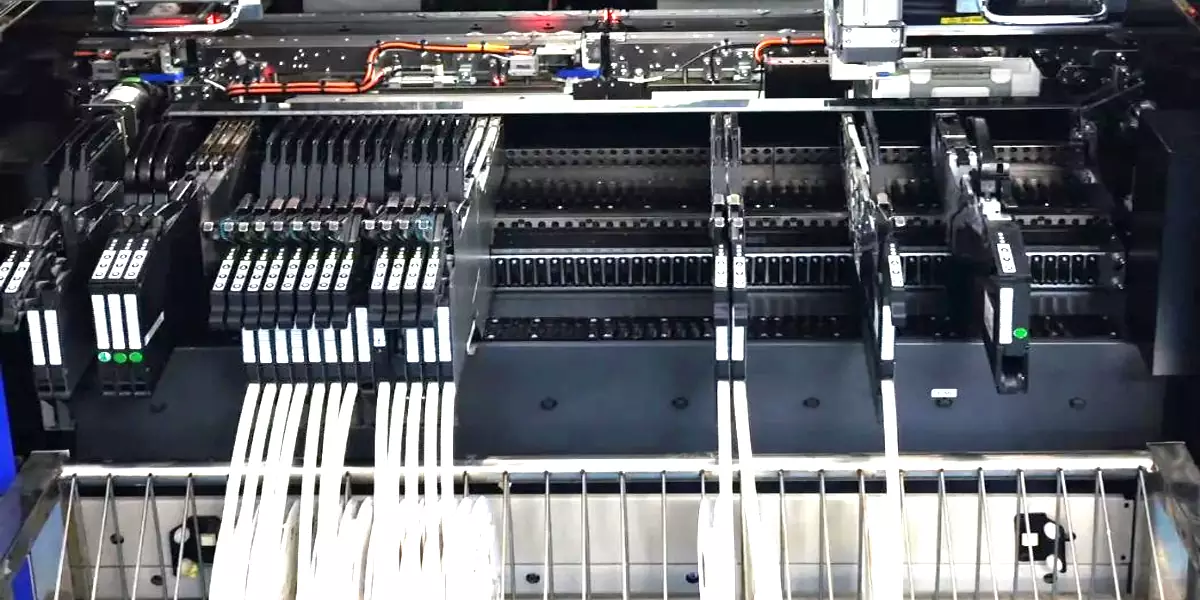
Electronic Manufacturing
Development of Electronic Manufacturing
Process technology: Electronic manufacturing involves various process technologies, including semiconductor processes, PCB printed circuit board, packaging and encapsulation technology, etc. Semiconductor processes involve crystal growth, etching, photolithography, ion implantation, and other steps that directly affect chip performance and production capacity. PCB manufacturing includes processes such as design, printing, gold plating, and perforation, which are related to the connection and communication of electronic components. Packaging technology involves various packaging forms such as BGA, QFN, CSP, etc., which play an important role in product heat dissipation, protection, and electrical performance.
Materials Science: There are various types of materials required for electronic manufacturing, including semiconductor materials, conductive materials, insulating materials, etc. The selection and purity of semiconductor materials are directly related to chip performance, while the performance of conductive materials affects the conductivity and stability of electronic components. The development of materials science is of great significance for improving the performance, reliability, and environmental adaptability of electronic manufacturing products.
Automation and Intelligent Manufacturing: Electronic manufacturing relies on automation and intelligent manufacturing to improve production efficiency and product quality. Automated production lines can achieve precision assembly, testing, and packaging, thereby reducing human intervention and improving consistency and stability. Intelligent manufacturing utilizes data analysis, artificial intelligence, and IoT technology to achieve real-time monitoring, optimization, and prediction of the production process, thereby better meeting market demand.
Environmental and safety technology: The chemicals and processes involved in electronic manufacturing pose challenges to the environment and employee health. Environmental technologies include wastewater treatment, exhaust gas treatment, and solid waste treatment to reduce adverse impacts on the environment. Security technology involves personal safety, equipment safety, and information security in the workplace, ensuring the sustainability and stability of the production process.
Application of emerging technologies: The electronic manufacturing industry continues to absorb emerging technologies such as 5G communication, the Internet of Things, wearable devices, etc., promoting industrial upgrading and innovation. 5G communication technology provides faster data transmission rates and lower latency, supporting intelligent manufacturing and remote operations. The Internet of Things technology enables interconnectivity between devices, improving the intelligence and controllability of the production process. Wearable devices combine electronic manufacturing with fields such as fashion and healthcare, expanding the breadth and depth of industry applications.
Quality Control System for Electronic Manufacturing
Quality control during the design phase: In the product design phase, the goal of quality control is to ensure that the product meets the expected performance and functional requirements. This includes every step from material selection to engineering design to ensure the manufacturability and maintainability of the product. Design review, prototype testing, and simulation analysis are commonly used methods to verify whether the design meets technical standards and industry norms.
Raw material and supplier management: The quality control system must ensure that the raw materials obtained from suppliers comply with product specifications. This includes establishing a list of qualified suppliers, conducting supply chain reviews, and regularly evaluating the quality of suppliers. The use of a traceability system can trace the source of raw materials for recall and investigation in the event of quality issues.
Production process control: Strict quality control measures during the production process can ensure product consistency and stability. The adoption of advanced manufacturing technology and automation equipment can reduce the possibility of human error. By implementing standard operating procedures (SOP), production line monitoring, and process validation, variability in production can be minimized to the greatest extent possible.
Testing and Inspection: The quality control system needs to ensure that products undergo sufficient testing and inspection to verify their performance and quality. This includes the use of various non-destructive testing methods (such as X-ray testing, ultrasonic testing, etc.) and functional testing. The calibration and maintenance of testing equipment are crucial for the accuracy of test results.
Defective product management and improvement: If defective products are found during the production process, the Electronic Manufacturing quality control system needs to have clear procedures for handling defective products. This includes isolating defective products, analyzing root causes, and taking corrective measures to prevent similar issues from happening again. At the same time, continuous improvement is also a key element of the quality control system. By collecting data and analyzing results, a continuous improvement plan is developed to improve the overall quality level.
Training and Certification: The quality control system needs to ensure that employees have sufficient skills and knowledge to perform their job tasks. Regular training and certification can enhance employees' awareness and sense of responsibility, ensuring they comply with quality standards and processes.

Electronic Manufacturing
The transformation of the global supply chain will have a profound impact on electronics manufacturer. Under the changing geopolitical and trade situation, electronic manufacturer will reassess the risks of their supply chains. At the same time, the application of digital and intelligent manufacturing technologies will promote the synergy of the electronic manufacturing supply chain, enhance its flexibility and responsiveness.