In the modern world, electronics have seen a rapid evolution that necessitates the development of more compact, lightweight, and flexible components. Enter Flexible Printed Circuits a technology that revolutionizes how electronic devices are designed and manufactured. In this blog, we will delve into what FPCs are, their benefits, applications, and reasons why they are becoming increasingly popular in various industries.
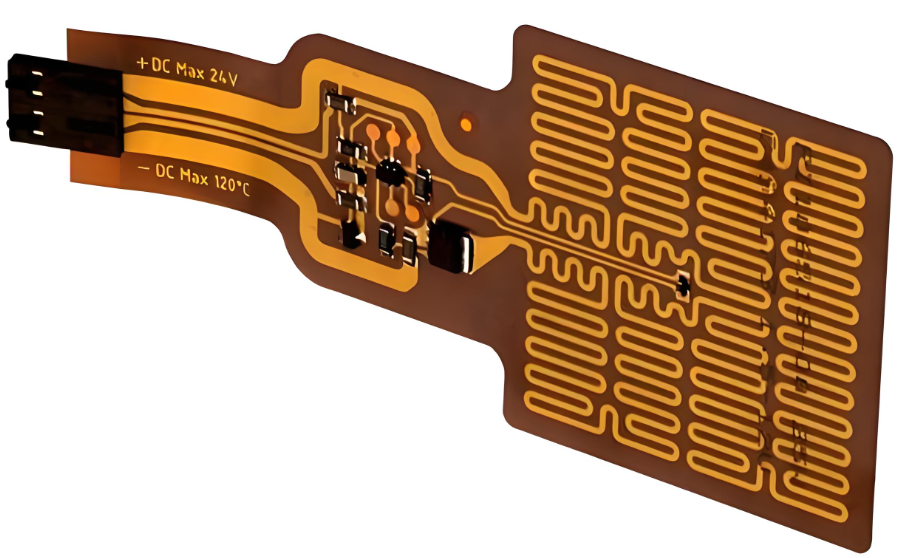
FPCB
What is a Flexible Printed Circuit?:
Flexible Printed Circuits are circuit boards designed to flex, bend, and fit into spaces where traditional rigid circuit boards would not work. Made from flexible substrates typically polyimide or polyester FPCs allow for complex electrical connections to be created in a lightweight form factor. They can incorporate all standard electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, into a very compact design.
Key Characteristics of FPCs:
Flexibility: As the name suggests, FPCs are flexible, allowing them to be bent or twisted without damaging the circuitry.
Lightweight: FPCs use lightweight materials, making them ideal for applications where weight is a consideration.
Compact Design: They can be designed to fit into tight spaces, making them perfect for complex assemblies.
Durability: The materials used in FPCs are resistant to high temperatures, chemicals, and moisture, ensuring long-lasting performance.
Complexity: Advanced manufacturing techniques allow for multi-layered circuits and intricate designs that can include both passive and active components.
Benefits of Using Flexible Printed Circuits
1. Space and Weight Efficiency
FPCs are an excellent solution for applications where space is at a premium. Their ability to be bent and shaped allows for unique layouts that can make efficient use of available space, especially in small devices like smartwatches, smartphones, and medical devices.
2. Space and Weight Efficiency
Flexible circuits are typically more resistant to mechanical stress. Due to their ability to flex and move without cracking or losing integrity, FPCs often exhibit increased reliability in dynamic environments where rigid boards may fail.
3. Enhanced Design Freedom
The flexibility of FPCs allows designers to create innovative and creative solutions that can enable new product concepts that were previously unachievable with traditional rigid boards. This freedom can speed up the design process and encourage innovation.
4. Cost-Effective in Mass Production
While the initial cost of designing and prototyping flexible circuits may be higher than rigid boards due to the specialized materials and manufacturing processes, FPCs can be extremely cost-effective in high-volume production runs. The minimized assembly costs and reduced component counts lead to lower overall production costs.
Applications of Flexible Printed Circuits:
FPCs are rapidly being adopted across various industries due to their unique advantages. Here are some key applications:
1. Consumer Electronics
From smartphones and tablets to laptops and wearables, FPCs are commonplace in consumer electronics, enabling compact designs and lightweight components.
2. Medical Devices
In the medical field, where space is critical, FPCs are used in devices like pacemakers, MRI machines, and disposable wearables that track health metrics, offering high reliability and performance.
3. Automotive Industry
Automotive applications include sensors, control units, and infotainment systems. As vehicles become more electronic with advanced features, FPCs are essential for reducing weight and maximizing space.
4. Aerospace and Military
In aerospace and military applications, FPCs provide lightweight, durable solutions that can withstand harsh environments while maintaining flexibility and reliability.
5. Industrial Equipment
Flexible circuits are utilized in industrial automation equipment for control panels, sensors, and devices where flexibility is vital due to movement or vibration.
Challenges in the FPC Market:
While the benefits of FPCs are considerable, there are also challenges in their manufacture and deployment:
Initial Costs: The upfront costs for developing flexible circuits can be high, particularly for low volume applications.
Design Complexity: Designing FPCs requires specialized knowledge and tools, making it critical to collaborate closely with experienced manufacturers.
Manufacturing Limitations: Some advanced designs may be challenging to manufacture at scale, necessitating continuous innovation in FPC technology.
Conclusion:
Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs) are driving innovation across various industries by providing solutions that are compact, lightweight, and adaptable. With an ever-growing demand for smaller and more efficient electronic devices, FPCs represent a promising future for electronics manufacturing.
Businesses looking to stay competitive in an increasingly technology-driven landscape should consider the advantages of adopting flexible circuits. By leveraging FPC technology, companies can push the boundaries of what is possible in their designs, leading to enhanced product offerings and improved market positioning. Whether you are designing consumer electronics, medical devices, or automotive applications, FPCs can unlock new avenues for creativity and functionality in electronic circuit design.
For engineers and designers exploring the world of FPC, understanding the unique advantages and challenges is crucial for successful deployment. As we look toward the future, the flexibility, efficiency, and reliability of FPCs are likely to play an essential role in the ongoing evolution of electronic devices.
If you're ready to explore the benefits of Flexible Printed Circuits for your project, reach out to IPCB for expertise in FPC design and manufacturing!