In PCB Bord Design, layout is a critical phase. The quality of the layout directly affects routing effectiveness, making it essential for a successful PCB Board Besign.
Layout methods can be categorized into two types: interactive and automatic. Typically, layouts start with an automatic process, followed by adjustments through an interactive approach. During layout, circuit gates may be reallocated based on routing needs, allowing for the optimal arrangement that facilitates wiring. Once the layout is finalized, design files and relevant information should be annotated back to the schematic to ensure consistency, aiding future documentation and design modifications. Additionally, updates on simulation data will support board-level verification of electrical performance and functionality.
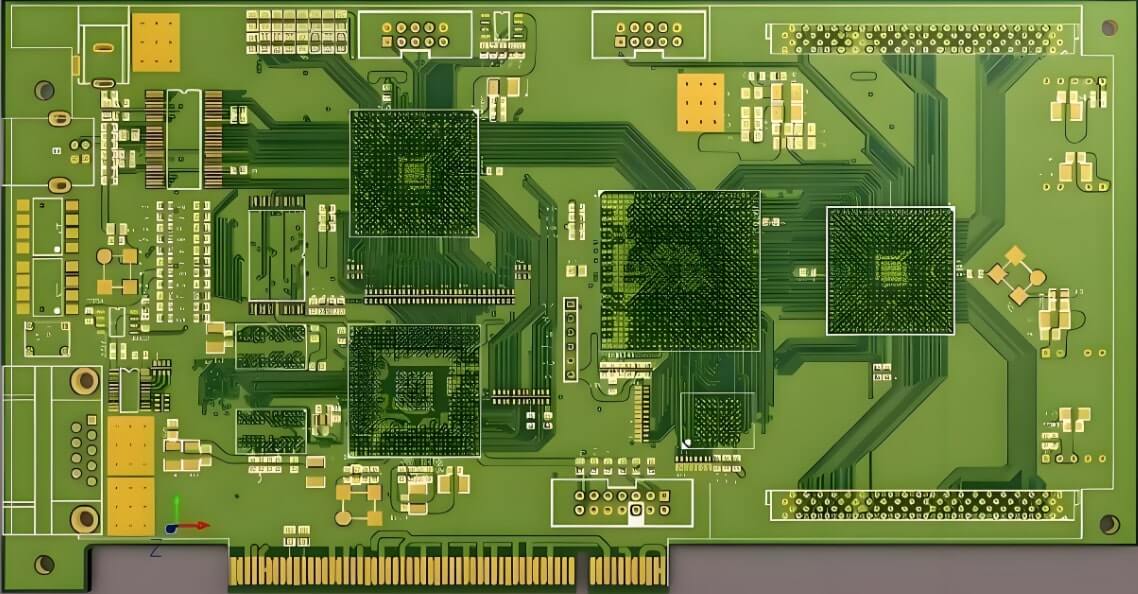
PCB
The success of a product relies on both internal quality and overall aesthetics; achieving excellence in both aspects is crucial.
On a PCB, component placement must be balanced, orderly, and neither top-heavy nor overly dense.
Ensure that the PCB dimensions match the manufacturing drawings and meet PCB production standards, including proper positioning marks.
Check for any conflicts between components in both 2D and 3D spaces.
Verify that the layout is organized, neat, and fully populated.
Components that require frequent replacement should be easily accessible, and the insertion of plug-in boards must be convenient.
Maintain appropriate spacing between heat-sensitive and heat-generating components.
Ensure that adjustable components are accessible.
Confirm the presence of heat sinks in areas requiring thermal management and ensure proper airflow.
Check for smooth signal flow and minimize interconnections.
Evaluate compatibility between connectors and mechanical designs.
Consider potential interference issues in routing.