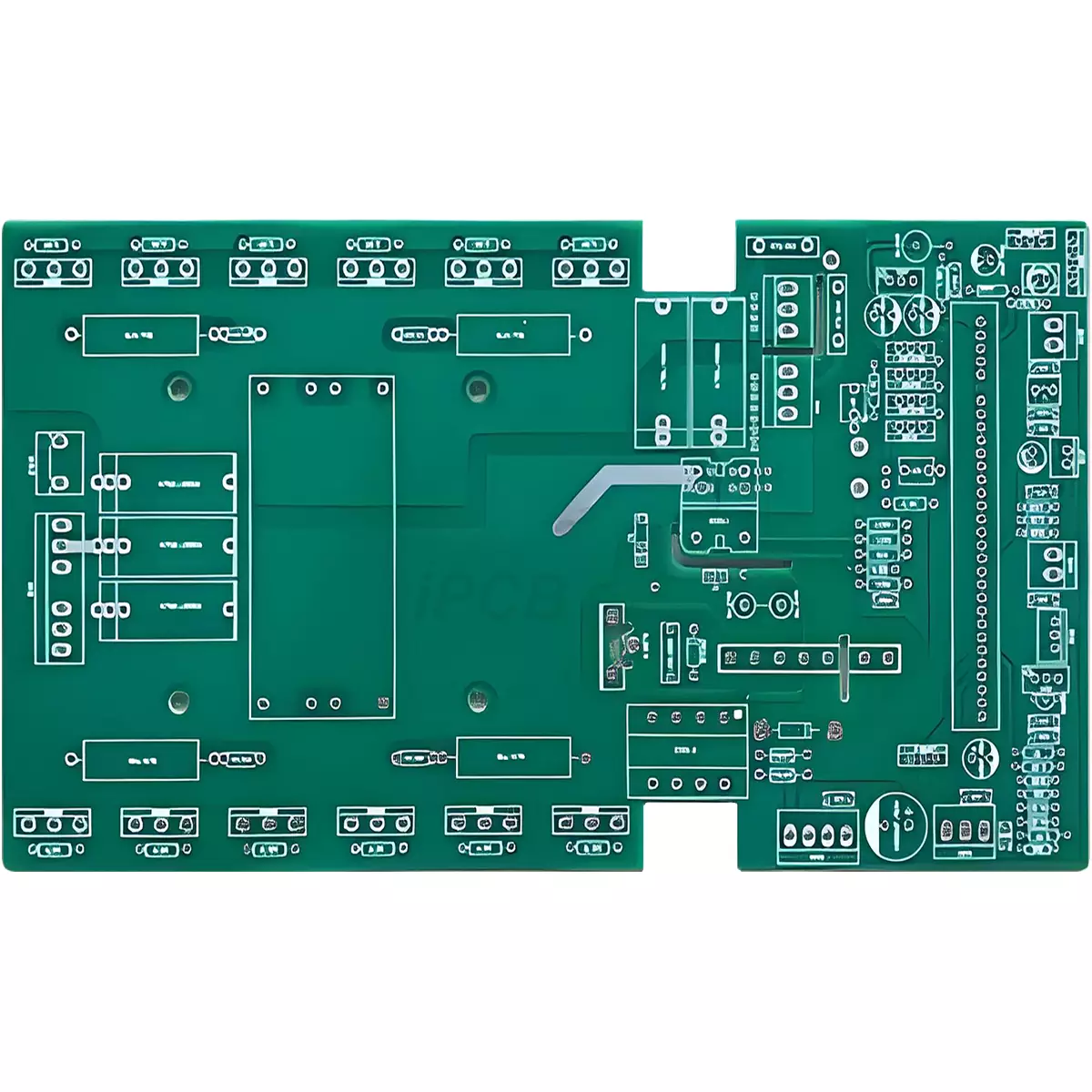
Product Name: Inverter PCB
Material: FR-4
Layers: 2layers
Thickness: 1.6mm
Copper thickness: 1oz
Surface technology: lead-free HASL
Minimum line width/spacing: 6/6mil
Minimum through-hole: 0.3mm
Solder mask: Green
Screen printing: White
Application: Power adapter
What is an inverter?
In power electronics technology, converting alternating current to direct current is called rectification, and converting direct current to alternating current is called inversion. Due to the photovoltaic effect, solar cells generate direct current. When the load is an alternating current device, an inverter is necessary for energy conversion. Photovoltaic inverter are power electronic devices used in photovoltaic power generation systems to convert direct current into alternating current.
Photovoltaic inverter can track the maximum output power of photovoltaic module displays, and integrate their energy into the grid or for electrical equipment applications with minimal conversion losses and optimal power quality
Photovoltaic inverter can track the maximum output power of photovoltaic module displays, and integrate their energy into the grid or for electrical equipment applications with minimal conversion losses and optimal power quality. The reliability, efficiency, and safety of photovoltaic inverter directly affect the power generation and operational stability of the entire photovoltaic power generation system, and are key equipment in the entire photovoltaic power generation system
The inverter is mainly composed of three parts: inverter PCB, logic control circuit, and filtering circuit. It mainly includes input interface, voltage starting circuit, MOS switch tube, PWM controller, DC conversion circuit, feedback circuit, LC oscillation and output circuit, load and other parts. Among them, the control circuit is responsible for the operation of the entire inverter system, the inverter circuit is responsible for converting DC power into AC power, and the filtering circuit is responsible for filtering redundant signals.
The high-frequency inverter uses small-sized and lightweight high-frequency magnetic core materials, greatly improving the power density of the circuit, thereby reducing the no-load loss of the inverter power supply and improving the inverter efficiency. Generally, the conversion efficiency of high-frequency inverter can reach over 90%. Excellent pure sine wave inverter provide AC power of higher quality than the grid, without electromagnetic pollution in the grid, with a wide range of applications, strong load capacity, excellent stability, and higher overall efficiency. High frequency pure sine wave inverter have a large market share.
Production of inverter
The production process of photovoltaic inverter mainly includes burning, installation, testing and other links, and the core technology is mainly reflected in control algorithms, circuit topology, industrial design, etc. In the production process, electronic pre-processing involving inverter PCB burning, testing, and protection is the core step, which requires high precision. Due to the high degree of automation of PCB circuit board assembly line equipment and relatively increased investment in fixed assets and personnel, some inverter enterprises with relatively small production capacity will prioritize outsourcing processing to improve capital utilization efficiency.
One of the important features of photovoltaic inverter is that the production line can flexibly switch between different powers. The production process of photovoltaic grid connected inverter in different power ranges remains basically the same, with the main difference being the specifications of the production line equipment. In the production of photovoltaic inverter, high-power inverter production lines can be backward compatible and quickly switch to low-power production lines for production. The transformation of a low-power production line into a high-power production line requires equipment replacement and debugging.
Classification of Photovoltaic inverter
According to the differences in the technical path and power level of photovoltaic inverter, they can be divided into centralized photovoltaic inverter, string photovoltaic inverter, distributed photovoltaic inverter, and micro inverter.
Centralized photovoltaic inverter are mainly used in centralized photovoltaic power generation systems. Their operation mode mainly involves connecting a large number of parallel photovoltaic modules through a DC combiner box to the DC input terminal of the same centralized inverter. After the centralized inverter completes maximum power point tracking, it is then inverted and connected to the grid. Centralized inverter typically have a single capacity exceeding 500kW, high single power and low cost, and have excellent grid regulation capabilities. But in cloudy, partially shaded, or single component failures, the application of centralized inverter will affect the efficiency and power generation of the entire photovoltaic power generation system. The maximum point power tracking voltage range of centralized inverter is relatively narrow, the flexibility of component configuration is insufficient, and the power generation time is short. They are mainly used in large-scale ground centralized photovoltaic power plants with uniform illumination.
The string inverter is mainly used in distributed photovoltaic power generation systems, and its operation mode is to track the maximum power point of several photovoltaic modules separately, and then invert them into the AC power grid through the string inverter. A single string photovoltaic inverter can have multiple maximum power point tracking modules, and its individual capacity is usually less than 100kW. The string inverter allows for voltage and current mismatch between strings with different maximum electrical power, thereby achieving higher power generation efficiency. And its volume and footprint are relatively small, mainly used in smaller distributed photovoltaic power plants.
Distributed photovoltaic inverter are mainly used in photovoltaic power plants in complex scenarios such as large ground, water, mountains, and hills. Their operation mode mainly involves pre installing multiple maximum power tracking control optimizers to achieve multi-channel maximum power tracking and optimization functions, and then converging to the distributed inverter. Distributed inverter significantly reduce the equipment cost of photovoltaic power generation systems by adopting decentralized optimization and centralized convergence inversion methods. Currently, distributed inverter are mainly used in some leading demonstration base projects, but they require dedicated machine rooms for heat dissipation and occupy a large ground area. Moreover, there is limited project experience and large-scale application has not been achieved.
Micro inverter, also known as component level inverter, are mainly used in distributed photovoltaics with smaller power generation scales. Their operation mode is that a single micro inverter only corresponds to a small number of photovoltaic modules, so as to finely adjust, monitor, and track the output power of each photovoltaic module, and then convert it into an inverter and merge it into the power grid. Micro inverter generally have a single capacity of less than 5kW. Due to their ability to accurately track the maximum power of individual components, they improve the overall efficiency of photovoltaic systems when there is partial shading or performance differences between components. On average, micro inverter systems have better conversion efficiency than centralized and string inverter. However, micro inverter are currently expensive and do not have a competitive advantage in terms of cost.
From the perspective of performance parameters, various types of inverter have relative application scenarios and advantages in their respective application scenarios. From the perspective of single watt cost, micro inverter>string inverter>centralized inverter>distributed inverter
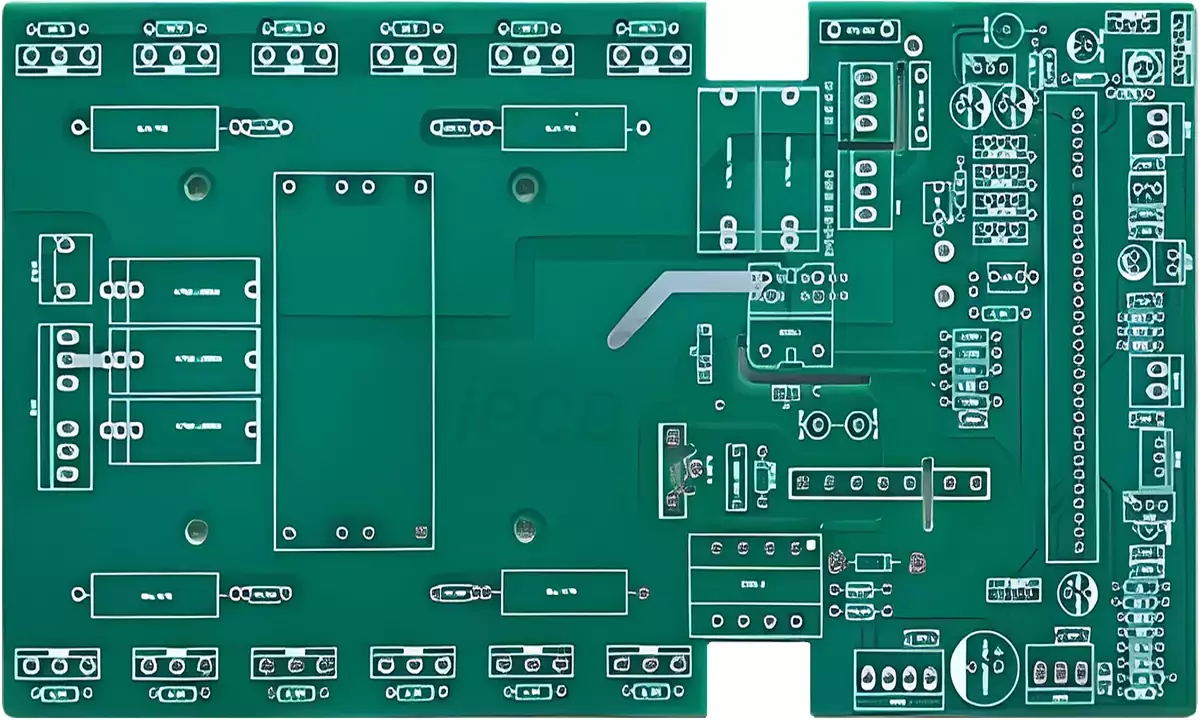
Inverter Circuit Board
What is an inverter PCB?
Inverter PCB is a PCB circuit board used for inverter and is an important component in the field of electronic engineering. Inverter is a critical electronic device that can convert DC electrical energy into AC electrical energy. inverter play a crucial role in the application of renewable energy systems such as solar power and wind power. It efficiently converts the DC energy collected by solar panels or wind turbines into AC power suitable for household and business use.
The inverter PCB board design is complex, integrating multiple functions and circuits. It usually includes rectifier circuits for processing DC input voltage, filtering circuits, and inverter circuits for converting DC power into AC power. At the same time, the inverter PCB will also integrate control circuits for precise adjustment of output voltage, frequency, and power, ensuring stable and efficient operation of the inverter. In addition, the protection circuit is also an indispensable part of the inverter PCB board, which can provide overcurrent, overvoltage, overtemperature protection for the inverter to prevent equipment damage due to abnormal conditions.
When manufacturing inverter PCB, engineers need to consider key factors such as electromagnetic compatibility, heat dissipation performance, and anti-interference ability to ensure that the circuit board can work stably and reliably in various environments and usage conditions. Therefore, the design and production of inverter PCB often require strict testing and validation to meet industry standards and safety regulations.
The inverter PCB board is the core component of the inverter, and its design and performance directly affect the efficiency and reliability of the entire inverter. In renewable energy systems, the inverter PCB is a key bridge connecting energy collection and conversion, ensuring the effective utilization and safe supply of energy.
Product Name: Inverter PCB
Material: FR-4
Layers: 2layers
Thickness: 1.6mm
Copper thickness: 1oz
Surface technology: lead-free HASL
Minimum line width/spacing: 6/6mil
Minimum through-hole: 0.3mm
Solder mask: Green
Screen printing: White
Application: Power adapter
iPCB Corporation provides support for PCB Prototype and Electronic Manufacturing. You can request consultation or quotation for PCB, PCBA and ODM here, please contact email: sales@ipcb.com
We will respond very quickly.