PCB panelization is a technique used in PCB manufacturing where multiple smaller printed circuit boards are grouped together to create a single array, referred to as a panel. This process is widely used in PCB production as it helps reduce both time and costs. In this article, we explore the key conditions, design factors, methods, types, and advantages of PCB panelization.
Introduction
PCB panelization is a manufacturing process where multiple smaller circuit boards are assembled into a single array to streamline production and improve efficiency. CNC machines, capable of handling large-sized PCBs, are optimized by placing multiple copies of smaller PCB designs together in a panel. Once production is complete, individual boards are easily separated for packaging or integration. This technique is widely used in PCB manufacturing as it reduces both time and costs.
What is a PCB Panel?
A PCB panel, or array, consists of multiple smaller PCBs connected together, which are later separated during the depanelization process. This technique reduces defects during assembly by allowing automated machines to work more efficiently. Panels can contain a single design (single-up) or multiple designs (multi-up). PCB panelization improves material utilization, reduces costs, and speeds up high-volume production by enhancing automated assembly processes.
When is PCB Panelization Required?
PCB panelization is required when producing small-sized PCBs, as it allows multiple copies of the design to be efficiently replicated on a single panel, minimizing the cost increase. This is especially useful for product designs with orders in the range of ten to hundred thousand units. Panelization helps overcome issues with small PCBs that cannot meet SMT fixture requirements, improving manufacturing convenience. It also increases fabrication yield, simplifies quality control, and allows automated machines to process multiple PCBs simultaneously, enhancing equipment utilization.
Combinations of PCB Panelization
PCB panelization can adopt different structures, each with its own advantages and challenges. The choice of structure depends on factors such as component density, equipment configuration, and production requirements. Here are some common combinations:
ABCD Combination
This method combines multiple single PCB orders into a single panel, often used for products like toys and home appliances. It increases production efficiency and reduces costs by streamlining manufacturing and minimizing inventory. However, it can lead to challenges in product differentiation on the assembly line and may affect overall quality if one board in the panel is defective.
AAAA Combination
The most commonly used panelizationmethod, the AAAA combination is compatible with all types of SMT manufacturers and product combinations. It offers the best manufacturability by optimizing panel production based on the highest number of SMT equipment. This combination also avoids issues related to pad orientation and maintains high printing quality, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
ABAB Combination
Typically used for medium-sized products like calculators and handheld devices, this combination involves 3 to 5 small PCB designs. It is suitable for products requiring multiple PCBs but is less commonly used than the AAAA and ABCD combinations.
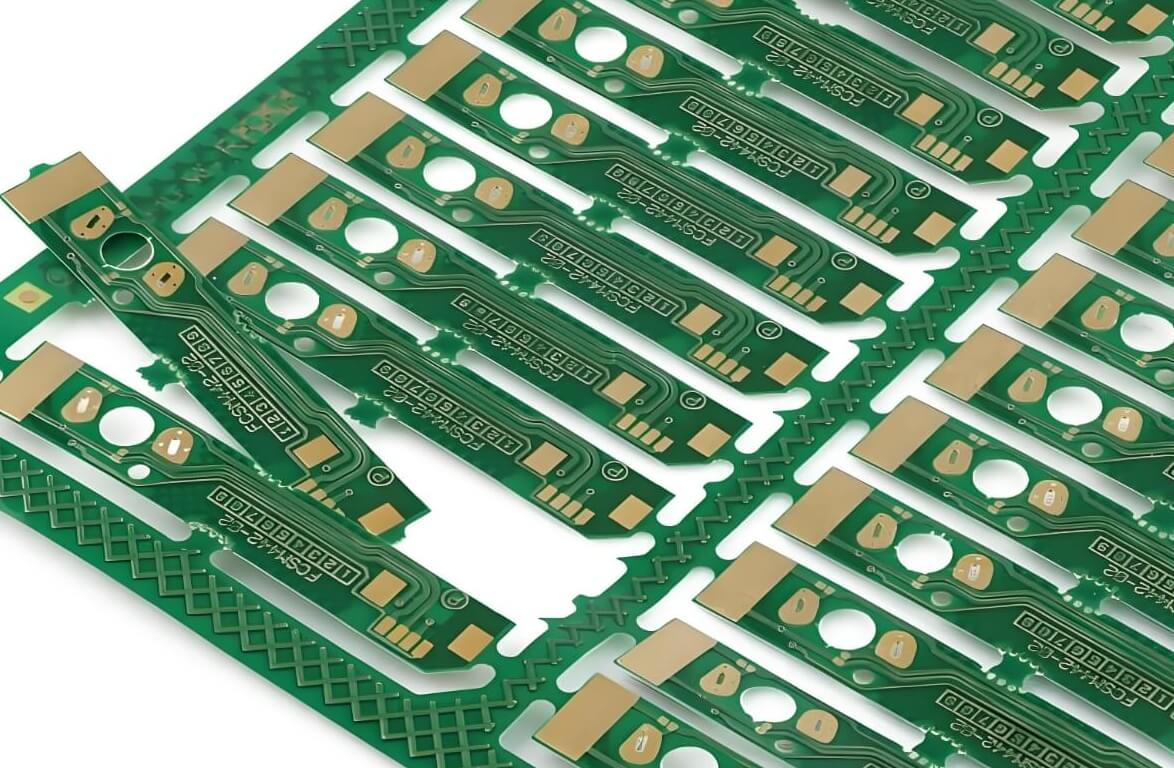
Penalized PCB
Depanelization Methods
Depanelization is the process of separating individual circuit boards from a PCB panel or array. This can be done through various techniques, with one popular method being:
V-Score Panelization
In this widely used technique, individual PCBs are divided by creating V-shaped grooves along the panel. An angled blade is used to cut about a third of the board’s thickness from the top and bottom. The remaining portion of the board between the grooves remains sturdy enough to hold the boards together. Since manual breaking can cause stress to the PCB and nearby components, a machine is typically used to complete the depanelization process.
Tab Routing Panelization
Tab routing is a technique used in PCB panelization when a V-groove approach is not suitable. It involves pre-cutting PCBs from the array while using perforated tabs to hold the boards in place. These tabs typically feature three to five holes. This method is especially beneficial for designs with edge-hanging components and can be easily broken by hand, eliminating the need for additional tools. Tab routing provides flexibility and convenience while maintaining the stability of the PCBs during the manufacturing process.
Solid Tab Panelization
Solid tab panelization involves adding sturdy tabs between each PCB in the array to increase the strength of the panel. However, the depaneling process requires specialized tools such as a depaneling router, laser cutter, or hook-shaped blade tool. The laser cutter, though precise, is costly and ineffective for boards thicker than 1mm. The router, while more affordable, can create dust and vibration during operation. The hook-blade tool is a less effective option prone to blade rotation. As a result, solid tab panelization is less commonly used compared to other methods.
The choice between V-scoring and tab routing for PCB panelization depends on several factors:
Time Use: Tab routing is time-consuming and labor-intensive, while V-scoring is faster and requires less machine time.
Edge Quality: Tab routing generally provides smoother edges, though minor roughness can be sanded away. V-scoring often leaves rough edges that may need additional sanding for smoothness.
Board Shapes: V-scoring works best for square or rectangular boards, while tab routing is better for irregular shapes.
Edge Components: V-scoring may not be suitable for PCBs with edge-hanging components or components close to the edges, where tab routing may be more appropriate.
Waste: V-scoring produces less material waste, making it more cost-effective compared to tab routing.
Both methods can be combined in some cases to take advantage of their respective benefits.
There are three main types of PCB panelization:
Order Panelization: This is the most common type, where a single PCB design is replicated across the entire panel. It is highly compatible with various product combinations and fabrication guidelines. While there may be some processing challenges, the final product quality remains intact.
Rotation Panelization: Used for irregularly shaped PCB designs, circuit boards are rotated 90 or 180 degrees to optimize material usage and reduce costs. However, this type can reduce assembly efficiency and complicate visual inspection, potentially affecting the quality of the boards.
Combination Panelization: Also known as characteristic panelization, this method involves combining different types of circuit boards based on specific combination principles. It is ideal for designs with various board combinations, such as those found in toys and household appliances. The three common combinations are AAAA, ABAB, and ABCD.
The advantages of PCB panelization extend beyond fitting smaller boards into standard production processes, enhancing production efficiency. Key benefits include:
Time and Cost Savings: PCB panelization is ideal for mass production, reducing both time and cost by enabling the handling of multiple smaller boards as part of a larger sheet.
Increased Efficiency: It allows for faster and more efficient production, as boards are fabricated using the standard size, reducing time and cost per unit.
Design Flexibility: Designers can incorporate unique designs into prototypes, achieving more efficient and cost-effective outcomes.
Protection: PCB panelization helps protect circuit boards from shocks and vibrations during the assembly process, ensuring the safety of the boards in challenging environments.
PCB panelization is a technique used in the production of small circuit boards to enhance efficiency and consistency. Multiple small PCBs are connected to form a larger panel, allowing manufacturers to assemble several boards at once. When implemented correctly, this technique boosts productivity and ensures the high quality of the circuit boards.