PCB circuit board is an indispensable and important part of electronic products. Different application scenarios require different types of PCB circuit boards. High-frequency boards and
high-speed boards are two special types of PCB circuit boards,
each with unique application scenarios and advantages.
1. Definition and characteristics
High frequency board:
Application areas: radio communication radar, satellite communication, etc.
Operating frequency: usually over 500MHz.
Plate thickness: relatively thin.
Line width and line spacing: thinner than ordinary PCB circuit boards.
Dielectric constant: relatively small, reducing signal loss, improving signal transmission rate and reception importance.
Commonly used materials: RO4350B, RO4003C, F4B, etc.
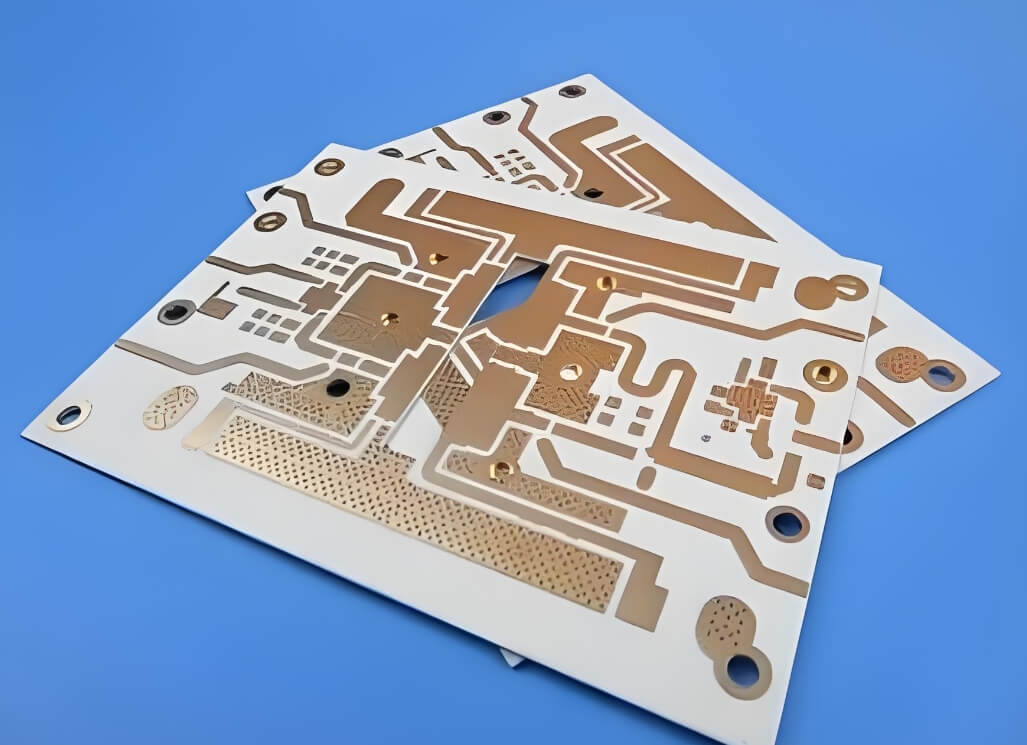
High Frequency Board
Application areas: computer motherboards, industrial computers, measurement and control instruments, etc.
Operating frequency: The modulation and demodulation frequency is low, but the rate is high, usually at the Gbps level.
Board thickness: relatively thick to effectively suppress EMI (electromagnetic interference).
Line width and line spacing: The line length is better, and the line width and line spacing can be appropriately increased.
Commonly used materials: FR4, PI, etc.
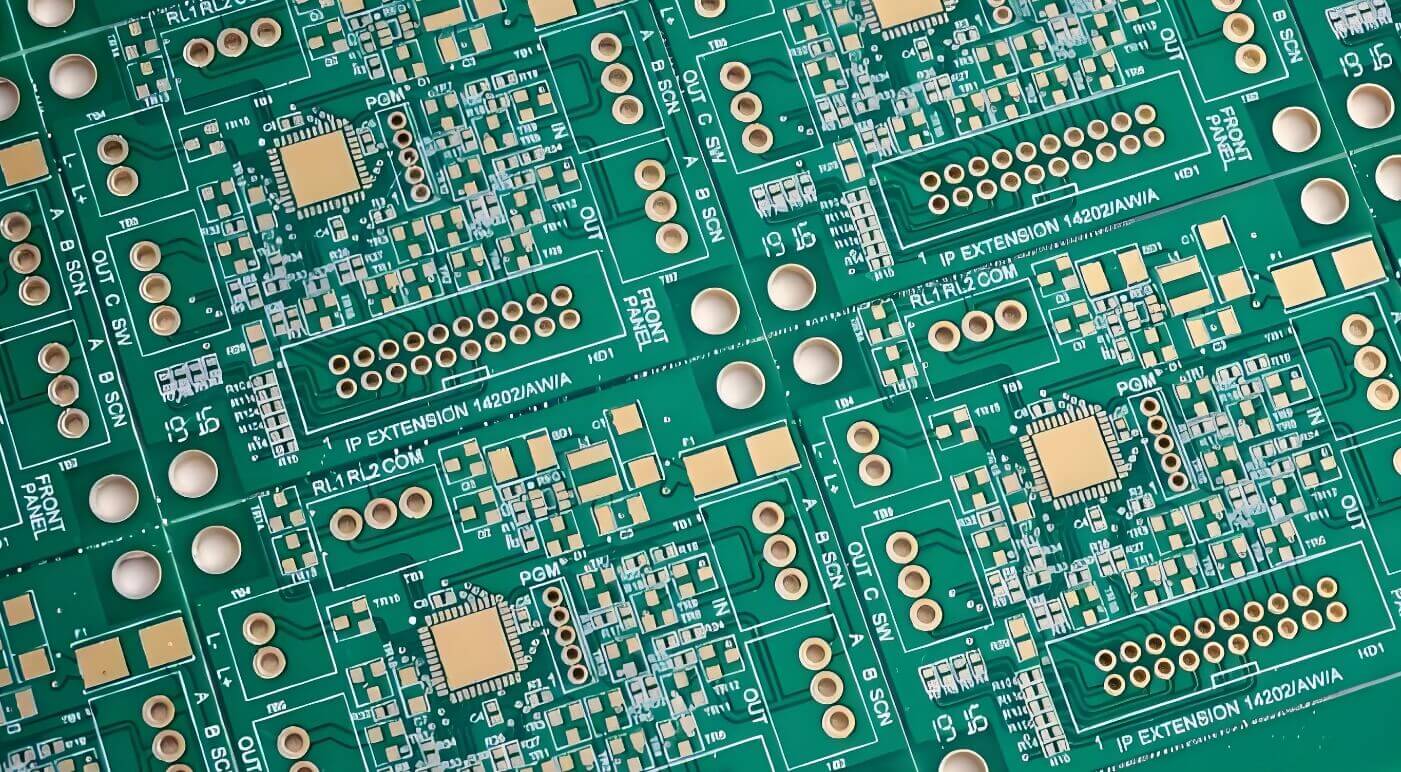
High Speed Board
2. Main differences
Frequency range:
High frequency board: operating frequency exceeds 500MHz.
High-speed board: modulation and demodulation frequency ranges from tens of MHz to GHz level.
Line width and plate thickness:
High frequency board: thinner line width, line spacing, and thinner board thickness.
High-speed board: line width and line spacing can be appropriately increased, and the board thickness is thicker.
Material:
High frequency board: Commonly used materials such as RO4350B, RO4003C, F4B, etc. have small dielectric constants.
High-speed board: Commonly used materials such as FR4, PI, etc., whose materials are usually better than ordinary PCB circuit boards, such as FR4 high TG material.
Application scenarios
High frequency board:
It is widely used in radio communication, radar, satellite communication and other fields.
In summary, High-Frequency and High-Speed PCB circuit boards serve distinct purposes in the electronics industry. High-frequency boards are designed for signals above 1 GHz, focusing on materials and construction that minimize signal loss and ensure integrity in RF applications. On the other hand, High-speed boards cater to rapid data transmission, managing signal integrity and crosstalk within lower frequency ranges. Understanding these differences is essential for engineers to select the appropriate board type for their specific applications, especially as the demand for advanced electronic solutions continues to rise. For further insights, consider exploring additional resources on PCB design and technology.