In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics manufacturing, Hybrid Printed Circuit Boards have emerged as a critical technology that meets the complex demands of modern applications. With over 20 years of experience in PCB design and manufacturing, I have witnessed the transformative impact that hybrid PCBs have had on the industry. This blog will explore what hybrid PCBs are, their advantages, applications, and the latest innovations in this exciting field.
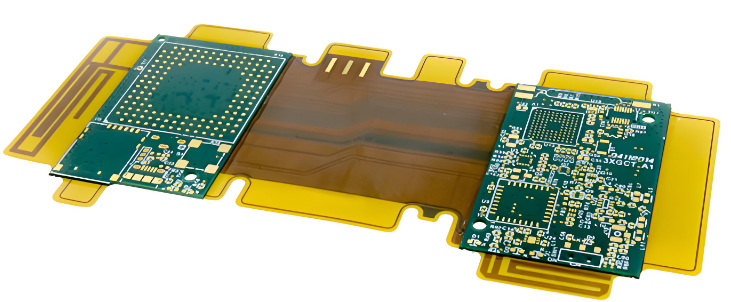
Hybrid PCB
What Are Hybrid PCBs?
Hybrid PCBs combine two or more types of substrate materials within a single circuit board. Typically, these materials are a mix of rigid and flexible substrates, such as FR-4 (a common rigid PCB material) and polyimide (often used for flexible circuits). The integration of these materials allows for greater design flexibility and the possibility of creating boards that are not only lightweight and compact but also capable of withstanding a variety of environmental stresses.
Advantages of Hybrid PCBs
Space Efficiency: Hybrid PCBs enable designers to create multi-layer, compact devices that maximize space, making them ideal for portable electronics such as smart phones, tablets, and wearable devices.
Weight Reduction: The combination of rigid and flexible substrates contributes to overall weight reduction, which is particularly crucial in industries like aerospace and automotive, where every gram counts.
Enhanced Durability: Hybrid PCBs can better withstand mechanical stress, temperature variations, and environmental factors compared to traditional single-material PCBs. This robustness enhances the longevity of the devices they power.
Design Versatility: The ability to incorporate various materials allows for unique design features, such as 3D shapes and custom layouts, facilitating innovations in product design.
Cost-Effectiveness: Despite the perception that hybrid PCBs may be more expensive to manufacture, their ability to integrate multiple functions into a single board can lead to overall cost savings by reducing assembly time and materials.
Applications of Hybrid PCBs
Hybrid PCBs are finding application across a diverse range of industries:
Consumer Electronics: In smart phones and tablets, hybrid PCBs allow for more functionality in a smaller footprint.
Medical Devices: The medical industry benefits from hybrid PCBs ability to produce compact and flexible designs that are essential for portable diagnostic equipment and implants.
Aerospace and Defense: The rigorous demands of these sectors necessitate the durability and lightweight characteristics of hybrid PCBs.
Automotive: As vehicles become smarter and more connected, hybrid PCBs are integral to the growing number of electronic systems in modern cars, such as infotainment and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Latest Innovations in Hybrid PCBs
The field of hybrid PCB manufacturing is rapidly advancing, thanks to developments in materials science and manufacturing techniques:
Advanced Materials: New high-frequency and low-loss materials are being developed, which improve signal integrity and performance for RF applications.
3D Printing: The rise of additive manufacturing allows for the rapid prototyping of hybrid PCBs, enabling more complex geometries that were previously difficult to achieve.
Embedded Components: The trend of embedding passive and active components within the PCB layers is gaining traction, reducing assembly time and enhancing performance.
Environmental Sustainability: Much of the new research focuses on using eco-friendly materials and processes, responding to the electronics industry's increasing emphasis on sustainability.
Conclusion
As the demand for more complex and efficient electronic devices continues to grow, hybrid PCBs stand out as a critical solution in addressing these challenges. Their unique capabilities enable manufacturers and designers to innovate without compromising on performance or reliability. With the incorporation of advanced materials, improved manufacturing techniques, and a commitment to sustainability, hybrid PCBs will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in the future of electronics manufacturing.