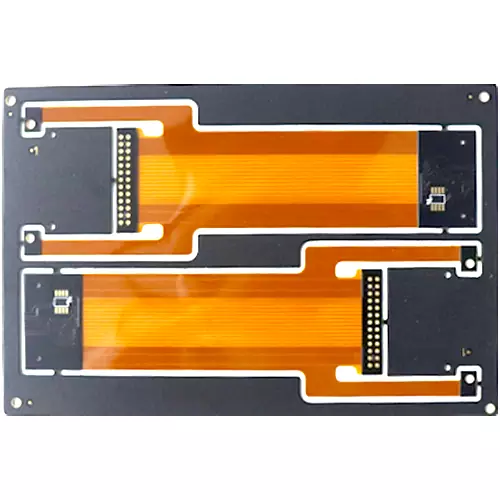
Product Name:Rigid-Flex PCB
Material:FR-4+PI
Thickness: 0.2mm+0.8mm
Copper thickness: 1OZ
Surface technology: Immersion gold
Solder mask: White/Green
Silk screen: White
Minimum line width/spacing: 5mil
Minimum through-hole: 0.2mm
Application: Consumer Electronics, Automotive Electronics, Industrial Automation, Medical Equipment, Communication Equipment
What is rigid flex pcb?It also known as rigid-flexible printed circuit board, is a circuit board that combines the advantages of a flexible circuit board (FPC) and a rigid circuit board (PCB). It uses a unique process to seamlessly integrate flexible circuits with rigid circuits, thus combining the characteristics of both. Rigid-flex boards are ideal for many electronic products because they can be bent and folded and have excellent mechanical stability.
Classic structure of rigid flex pcb
LPI (Liquid Photoimageable): This is a light-sensitive material that can be exposed to form the desired circuit pattern through a development process.This layer is usually coated on the surface of the substrate and is the outermost part of the entire FPC structure.
Copper:This is the main material that forms the conductor of the circuit.The copper foil is pasted under the LPI layer and the unwanted parts are removed through an etching process, leaving the desired circuit pattern.
FR4 (Flame Retardant Grade 4):This is a rigid layer used to enhance the rigidity and stability of the FPC. It is located underneath the copper foil and acts as a support.
Prepreg:This is a semi-cured sheet material containing resin and fibre reinforcement. When heated, it binds to the resin in neighbouring layers to enhance the mechanical strength and electrical properties of the entire FPC.
Polyimide (polymide): This is a polymer material that is resistant to high temperatures and chemicals. It is located below the prepreg and is used as an insulating layer.
Adhesive:This is an adhesive used to bond materials between different layers. It is located below the polyimide layer.
Polyimide:This is another insulating layer and is located below the adhesive.
Copper foil: This is another layer of electrically conductive material and is located below the polyimide.
Adhesive: This is another layer of adhesive, located below the copper foil.
Polyimide: This is the last layer of insulating material, located below the adhesive.
Prepreg: This is the last layer of semi-cured material and is located below the polyimide.
Copper foil: this is the last layer of conductive material and is located below the prepreg.
FR4: This is the last layer of rigid material and is located below the copper foil.
Copper Foil: This is the bottom layer of conductive material and is located underneath the FR4.
LBI (Liquid Photoimageable): This is another photosensitive material, similar to the LPI layer. It is located below the copper foil and is the innermost part of the entire FPC structure.
Process Flow
1.Design and pre-preparation
-Design phase: Use CAD software for circuit design to ensure accurate alignment of rigid and flexible parts.
- Material Selection:Select the appropriate substrate material according to the product requirements, such as PI (polyimide), FR4, etc.
- Producing conductive layer:Produce conductive pattern by photolithography process.
2.Inner Layer Pattern Creation
- Inner Layer Pattern Transfer:Transfer the design pattern to the copper cladding board, commonly used methods include photolithography, laser direct imaging (LDI), etc.
- Etching process:Chemical etching is used to remove excess copper and form the desired circuit pattern.
3.Lamination
- Rigid Lamination:Pre-treated inner layer patterns are laminated with other rigid substrates.
- Flexible Lamination:Flexible substrates are combined with conductive layers, usually using a hot press process.
4.Drilling and Copper Plating
- Mechanical Drilling: Mechanical drilling of holes in specified locations for subsequent installation of components or interlayer connections.
- Copper plating: A layer of copper is plated on the hole wall by chemical or electrolytic plating to ensure a reliable electrical connection.
5.Outer Layer Graphics and Etching
- Outer Layer Fabrication: Similar to Inner Layer Fabrication, outer layer circuits are formed by graphics transfer and etching.
- Flexible Circuit Fabrication: Creates circuit patterns on a flexible substrate and protects the flexural properties of the flexible area.
6.Flexible and Rigid pcb Combination
- Combination Process: The manufactured flexible circuits are accurately aligned and combined with the rigid boards, commonly used methods include hot press combination, adhesive bonding, etc.
7.Surface treatment
- pad treatment: the exposed copper surface treatment, such as gold immersion, OSP (organic solder film), spray tin, etc., in order to enhance the soldering performance and prevent oxidation.
8.Testing and quality control
- Electrical testing: conduct circuit connectivity testing to ensure that there are no breaks or short circuits.
- Functional Test: Conduct functional test on the assembled board to verify the overall performance of the circuit.
- Quality Inspection: Check the appearance, size, alignment between layers, etc.,to ensure that the product quality meets the standards.
9.Assembly and Finished Product
- Component Mounting: Mount components via SMT (Surface Mount Technology) or THT (Through Hole Mount Technology).
- Final Test: Comprehensive functional tests are conducted to ensure that the product meets all technical requirements before delivery.
Advantages of rigid flex pcb
1.Compact structural design
As electronic devices increasingly seek miniaturisation and flexibility, rigid flex pcb, with their versatility, can be easily bent and folded to fit into the internal space of small devices and accurately connect micro-components. This miniaturised design not only makes the device lighter, but also enhances its portability.
2.Improve system reliability
Since rigid flex pcb reduces the use of solder joints and board-to-board connectors, the risk of connection impedance is reduced.At the same time, the connection between the rigid PCB and the flexible PCB layer is firm and reliable, which further reduces the possibility of circuit failure, thus enhancing the reliability of the entire electronic system.
3.High space utilisation
Rigid flex pcb take advantage of the built-in interconnect circuits in the flexible PCB substrate to provide more wiring space.This makes it particularly suitable for application scenarios with compact designs, as there is no need for excessive space to accommodate wiring harnesses and large-sized connectors, thus improving space utilisation.
4. Reduced Overall Cost
While the initial cost of a rigid-flex pcb may be higher than a regular rigid PCB,it is more economical to assemble.Due to its smaller size and fewer connections, rigid-flex boards require fewer materials, parts and connector assemblies during assembly, which reduces the cost of purchasing and assembling the end product.In addition,this helps to reduce total manufacturing costs for assembly and logistics.
5.Testing Convenience
The sub-circuits of a rigid-flex pcb are already connected to each other,making it easy to perform automated testing.This type of testing enables manufacturers to identify and troubleshoot connectivity issues in a timely manner before assembling the components, thus avoiding unnecessary waste and expense.
6.Enhanced Design Flexibility
Rigid-flex pcb supports 3D design and multi-layer flexible PCB circuits, making them highly flexible and adaptable to a variety of small devices. Therefore, the device design is no longer limited by the specific layout of the rigid PCB board, but can be bent and folded according to the actual application requirements to meet the use of different scenarios.
7.High temperature resistance and harsh environment
The rigid-flex pcb is made of highly thermally stable polyimide material and therefore can withstand high temperature environments.At the same time, it combines the advantages of rigid PCBs and flexible PCBs with excellent resistance to radiation, hazardous oils and chemicals, as well as extreme shock, vibration and other harsh industrial conditions. This makes rigid flex pcb particularly suitable for use in equipment that may be subjected to excessive movement and vibration.
However, rigid-flex pcb is not without their drawbacks. The first problem is that the production process is complex and challenging, resulting in long production runs, low yields, and the need to invest in materials and human resources, which drives up costs and extends production lead times.Secondly, in the soldering and assembly process, the rigid-flex boards are spliced together,requiring components to be mounted and soldered in the rigid board area, while the fpc area relies on the rigid board to provide the necessary support. In addition, the reliability of a rigid-flex circuit board is greatly affected by environmental factors, such as changes in temperature and humidity, which can adversely affect the performance and stability of the circuit. Finally, in the event of a rigid-soft board failure, it can be difficult to repair,often requiring specialised repair services and high replacement costs.
Uses of Rigid-Flex PCB
Industrial -Rigid-flex pcb is used in a wide range of industrial, military and medical applications.These industrial components often require precision, safety, and durability,so Rigid-Flex PCBs need to have high reliability,high accuracy, low impedance loss, excellent signal transmission quality, and long service life.However,they are relatively costly due to the complexity of the process and limited production volumes.
Mobile Communication Devices - In mobile phones, rigid-flex pcb is commonly used in the hinge area of folding mobile phones, camera modules, keypads and RF modules. These applications require boards that can be bent and folded while maintaining stable signal transmission and circuit performance.
Consumer electronics - In consumer electronics, digital cameras (DSC) and digital video cameras (DV) are typical representatives of rigid flex pcb applications. From the performance point of view, the combination of rigid flex pcbs can be three-dimensional connection of different PCB hard boards and components, thereby increasing the total use of PCB area under the same line density,improve circuit carrying capacity, and reduce the limitations of signal transmission at the point of contact and assembly errors. In addition, its thin and flexible characteristics help reduce product size and weight.
Automotive Manufacturing - In the automotive industry, rigid-flex pcb is commonly used for key connection motherboards on steering wheels,connecting the screen of automotive video systems to the control panel, connecting the operation of door audio or function keys, reversing radar image systems, sensors (including air quality, temperature and humidity,and special gas regulation,etc.), automotive communication systems, satellite navigation, and connecting the rear seat console to the front. navigation, rear seat control panel and front-end controller connection boards, and external detection systems.These applications require boards with a high degree of reliability and stability to adapt to the complex and changing environment of the car.
Product Name:Rigid-Flex PCB
Material:FR-4+PI
Thickness: 0.2mm+0.8mm
Copper thickness: 1OZ
Surface technology: Immersion gold
Solder mask: White/Green
Silk screen: White
Minimum line width/spacing: 5mil
Minimum through-hole: 0.2mm
Application: Consumer Electronics, Automotive Electronics, Industrial Automation, Medical Equipment, Communication Equipment
iPCB Corporation provides support for PCB Prototype and Electronic Manufacturing. You can request consultation or quotation for PCB, PCBA and ODM here, please contact email: sales@ipcb.com
We will respond very quickly.